链表
介绍
链表(LinkedList):是一种线性数据结构,其中的每个元素都是一个节点对象,各个节点通过引用相连接。引用记录了下一个节点的内存地址,通过它可以从当前节点访问到下一个 节点。链表的设计使得各个节点可以被分散存储在内存各处。
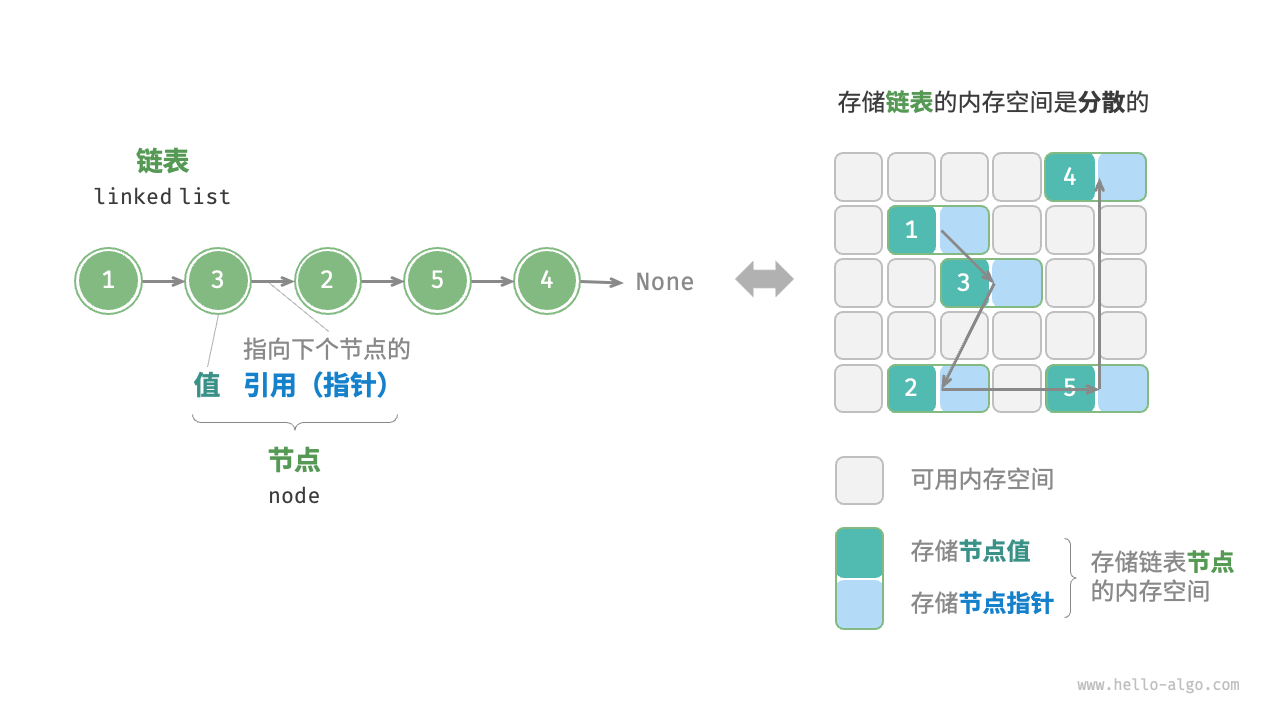
链表通常由链表节点ListNode对象组成,每个节点通常包含节点的值val和下一个节点的引用next。
// listNode.js
export default class ListNode {
constructor(val, next) {
this.val = val || 0;
this.next = next || null;
}
}
链表通常有如下规定:
- 首个节点被称为头结点(head),最后一个节点被称为尾结点(tail),一般而言尾结点的
next为空。 - 链表的长度就是节点的长度。
链表一般有三种类型:
- 单向链表:即普通链表。
- 双向链表:链接节点除了保存
next下一个节点的引用,还报错prev上一个节点的引用。 - 循环链表:在普通链表的基础上,首尾相连,即尾结点的引用指向头结点。
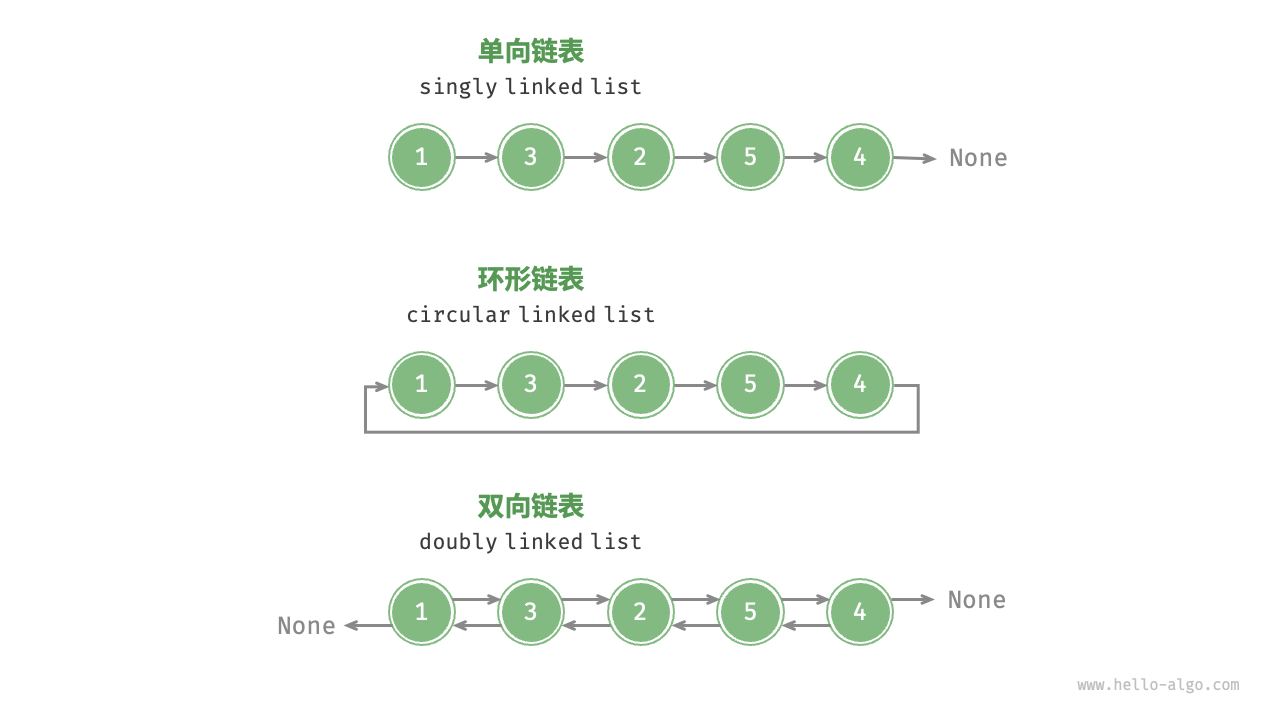
单向链表
单向链表:由ListNode节点组成,通常只有一个val(节点的值)、next(下个节点的引用)组成。单向链表是实现双向链表、循环链表的基础。 对单向链表而言,其一般有如下属性或方法:
_size: 内部属性,链表的长度。_head:内部属性,链表的头结点。push(val):方法,向链表尾部添加节点。insert(val, index):方法,向链表指定索引位置添加节点。成功插入返回true,反之返回false。remove(val):方法,移除指定值的节点。removeAt(index):方法,在链表中移除指定索引的节点。getNodeAt(index):方法,在链表中获取指定索引位置的节点。成功获取返回节点,反之返回null。getSize():方法,返回链表的长度。getHead():方法,返回链表头结点。isEmpty():方法,判断链表是否为空,为空返回true,反之返回false。indexOf(val):方法,根据节点的值,返回其节点的索引位置,不存在则返回-1。toString():方法,输出链表为字符串形式,用逗号分隔。
链表初始化:
export default class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this._head = null;
this._size = 0;
}
}
push(val)方法:向链表尾部添加节点。
export default class LinkedList {
push(val) {
const node = new ListNode(val);
// 1、链表为空时,直接赋值给头结点
// 2、链表不为空时,遍历至链表尾部并赋值
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this._head = node;
} else {
let current = this._head;
while(current && current.next !== null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = node;
}
this._size++;
}
}
insert(val, index)方法:向链表指定索引位置添加节点。
export default class LinkedList {
insert(val, index) {
if (!this._isSafeIndex(index, true)) {
return false;
}
// 1、当在头结点插入时,只需要改变头结点的引用即可。
// 2、当在非头结点插入时,首选需要找到待插入位置的上一个节点,然后改变引用即可。
const node = new ListNode(val);
let current = this._head;
if (index === 0) {
node.next = current;
this._head = node;
} else {
const prev = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
node.next = current;
}
this._size++;
return true;
}
getNodeAt(index) {
if (!this._isSafeIndex(index)) {
return null;
}
let current = this._head;
for (let i = 0; i < index && current !== null; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
_isSafeIndex(index, needLast) {
const lastResult = needLast
? index <= this._size
: index < this._size;
return index >= 0 && lastResult;
}
}
提示:其它方法实现,请参考单向链表完整实现代码
双向链表
双向链表是在单向链表的基础上实现的,它和单向链表的最大区别是:每个节点会保存上一个节点的引用prev,新增一个_tail表示尾结点。
双向链表节点doublyNode定义如下:
export default class DoublyNode extends ListNode {
constructor(val, next, prev) {
super(val, next);
this.prev = prev || null;
}
}
因为双向链表和单向链表存在差异,所以在一些方法和属性的实现上,会有所差别,如下:
_tail:独有,私有属性,表示双向链表尾结点。push(val):重写单向链表push(val)方法insert(val, index):重写单向链表insert(val, index)方法。removeAt(index):重写单向链表removeAt(index)方法。getTail():独有,获取双向链表尾结点。reverseToString():独有,从双向链表尾部输出链表为字符串形式,用逗号分隔。
双向链表初始化:
export default class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
this._tail = null;
}
}
push(val)方法:重写单向链表push(val)方法:
export default class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
push(val) {
const node = new DoublyNode(val);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this._head = node;
this._tail = node;
} else {
const tail = this._tail;
tail.next = node;
node.prev = tail;
this._tail = node;
}
this._size++;
}
}
insert(val, index)方法:重写单向链表insert(val, index)方法。
export default class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
insert(val, index) {
if (!this._isSafeIndex(index, true)) {
return false;
}
// 1、在头结点插入时,链表为空时,直接设置头结点和尾结点
// 2、在头结点插入时,链表为不空时,需要把新节点变成头结点,然后维护prev引用即可
// 3、在尾结点插入时,需要把新节点变成尾结点。
// 4、在非头、尾结点插入时,需要得到待插入节点的头结点,然后维护prev和next引用即可。
const node = new DoublyNode(val);
let current = null;
if (index === 0) {
if (this._head === null) {
this._head = node;
this._tail = node;
} else {
current = this._head;
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
this._head = node;
}
} else if (index === this._size) {
current = this._tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this._tail = node;
} else {
const prev = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
node.next = current;
node.prev = prev;
current.prev = node;
}
this._size++;
return true;
}
}
提示:其它方法实现,请参考双向链表实现代码
循环链表
循环链表是在单向链表的基础上实现的,它和单向链表的最大区别是:尾结点指向的地址非null,而是指向头结点。
因为循环链表和单向链表存在差异,所以在一些方法和属性的实现上,会有所差别,如下:
push(val):重写单向链表push(val)方法。insert(val, index):重写单向链表insert(val, index)方法。removeAt(index):重写单向链表removeAt(index)方法。
循环链表初始化:
export default class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
}
}
push(val)方法:重写单向链表push(val)方法:
export default class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
push(val) {
const node = new ListNode(val);
// 1、当链表为空时,把新节点当做头结点
// 2、当链表不为空时,迭代链表至尾结点,把新节点当做尾结点,并更新next引用指向头结点
if (this._head === null) {
this._head = node;
} else {
const current = this.getNodeAt(this._size - 1);
current.next = node;
}
node.next = this._head;
this._size++;
}
}
insert(val, index)方法:重写单向链表insert(val, index)方法。
export default class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
insert(val, index) {
if (!this._isSafeIndex(index, true)) {
return false;
}
// 1、在头结点插入,当链表为空时,直接把新节点当做头结点即可。
// 2、在头结点插入,当链表不为空时,把新节点当做头结点,然后找到尾结点并将其next指向新的头结点
// 3、在非头结点插入,正常找到待插入位置的上一个节点,然后正常插入节点即可。
const node = new ListNode(val);
let current;
if (index === 0) {
if (this._head === null) {
this._head = node;
node.next = this._head;
} else {
node.next = this._head;
current = this.getNodeAt(this._size - 1);
this._head = node;
current.next = this._head;
}
} else {
const prev = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
current = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
node.next = current;
}
this._size++;
return true;
}
}
提示:其它方法实现,请参考循环链表实现代码
链表典型应用
- 单向链表:常用于实现栈、队列、哈希表和图等数据结构。
- 双向链表:双向链表常被用于需要快速查找前一个和下一个元素的场景,例如:红黑树、B树,浏览器访问历史,LRU算法。
- 循环链表:循环链表常被用于需要周期性操作的场景,例如:时间片轮转调度算法,数据缓冲区。